Saluki SEC1106 series electrochemical workstation can provide an accurate measurement platform for battery research.
Constant current charge and discharge method, also known as chronopotentiometry. It can determine the charge-discharge curve, specific capacity, rate characteristics, cycle performance and other parameters of electrode materials. Usually, constant current charging is used first, then constant voltage charging, and constant current discharging after a period of time. It is best to test in a relatively constant temperature environment, and cycle charge and discharge many times to obtain stable data.
Figure 1 shows a typical setup of a Li-ion battery and an overview of the electrochemical processes during charging.
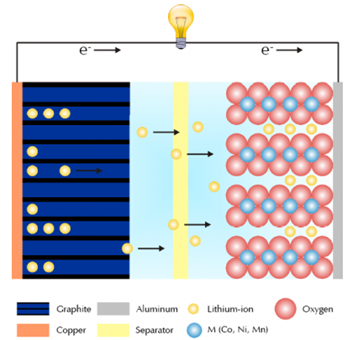
Fig.1 A brief schematic diagram of lithium ions during charging
The performance and lifespan of a Li-ion battery mainly depends on several parameters. Extreme temperatures can lead to material degradation. Exceeding the specified values of the battery rating, such as voltage, charging or discharging current, may cause irreversible reactions and cause the battery to overheat. The overall performance of the battery will also drop dramatically.
Charge-discharge Curve
Figure 2 shows a typical charge (green) and discharge (blue) of a coin cell battery. Plot voltage (dark) and current (light) against time. The battery is charged and discharged at a current of 40mA and a voltage between 2.75V and 4.2V.
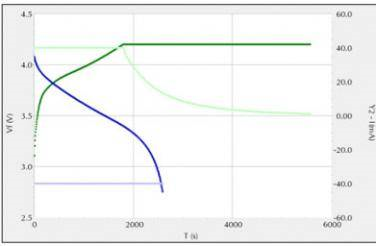
Fig.2 Charge-discharge curve of a coin cell battery (green: charging, blue: discharging)
Battery Cycle
A typical experiment to test the long-term stability of a battery is battery cycling. So the battery will be charged and discharged hundreds of times and then tested for capacity changes.
Figure 3 shows a standard battery charge-discharge experiment (CCD). The dark curve shows capacity. The light curve shows the percent capacity compared to the original.
The coin cell is first charged to 4.2V at a charge rate of 1.0C (40mA). Then keep the voltage constant for at least 72 hours or if the voltage reaches 1 mA. The battery was then discharged to 2.7V at a discharge rate of 1.0C. Repeat the experiment 100 cycles.
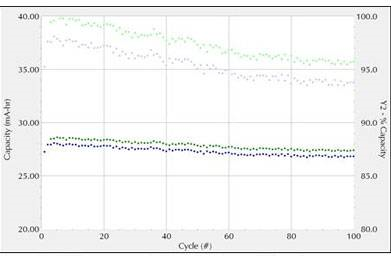
Fig.3 CCD test curve (green: charging, blue: discharging)
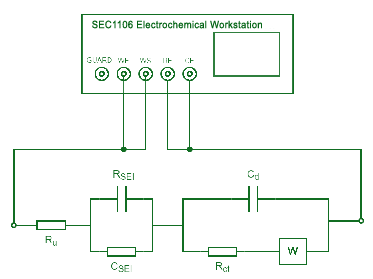
EIS Test
The AC impedance method is a method that uses a small-amplitude AC voltage or current to disturb the electrode to conduct electrochemical tests. From the obtained AC impedance data, the corresponding electrode reaction parameters can be calculated according to the simulated equivalent circuit of the electrodes.
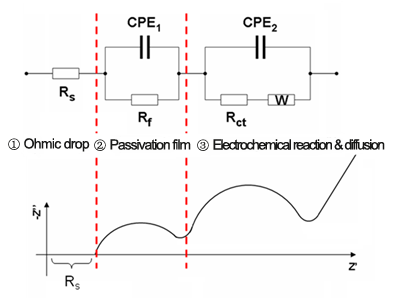
Fig. 4 EIS diagram of lithium battery
The basic idea of using EIS to study electrochemical systems: treat the electrochemical system as an equivalent circuit, use EIS to determine the composition of the equivalent circuit and the size of each component, and then use the meaning of these electrochemical components to analyze the electrochemical process.



