Research direction: vibration modal analysis
Experiment content:
Shear type (d15) piezoelectric strips are used to simulate linear shear force. Based on the characteristics of modal symmetry, by rationally designing the distribution position, polarization direction and electric field direction of multiple d15 piezoelectric strips, selectivity can be achieved can excite any vibration mode of the structure. Taking a stainless-steel rod with a rectangular cross-section as an example, different excitation methods are used, and only a pair of d15 piezoelectric strips are used to complete the selective excitation of the bending, torsion, and longitudinal vibration modes of the rod.
Test purpose: to verify the feasibility of the method and ensure that the target mode can be selectively excited.
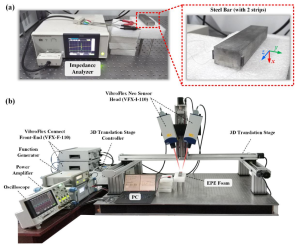
Test equipment: a pair of shear type (d15) piezoelectric strips, rectangular cross-section stainless steel rods, signal generator, SLA-HV-200S power amplifier, oscilloscope, etc.
Experiment procedure:
As shown in the figure, a continuous sinusoidal electrical signal is generated by a function generator. After amplification by a power amplifier, a pair of shear-type (d15) piezoelectric strips pasted on a rectangular stainless-steel rod are driven to produce continuous shear deformation, thereby achieving distributed Line-like shear force driven. By designing the polarization direction, electric field direction, arrangement position and other parameters of the piezoelectric strip, the bending mode, torsion mode and longitudinal vibration mode of the rectangular cross-section rod can be selectively excited. The vibration frequency response spectrum of the rectangular rod is measured by a Doppler laser vibrometer and collected by an oscilloscope. The frequency scanning, laser scanning, acquisition and other processes in the experiment are automatically completed through the Labview program written on the laptop computer.
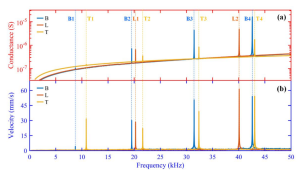
Test Results:
Three curves of different colors represent the velocity response spectrum of a rectangular cross-section rod measured by a laser vibrometer under three excitation modes. It can be seen that under the designed excitation method, the bending (B), torsion (T), and longitudinal vibration (L) modes can be selectively excited with quite high purity, which helps to distinguish the resonance frequency close to modal.